What is Governance Risk Management and Compliance (GRC)?
- Vignesh Prem
- 2 days ago
- 10 min read
Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance (GRC) is an integrated strategy that aligns an organization's decision-making (Governance), its ability to manage threats (Risk Management), and its adherence to laws and regulations (Compliance). It combines these siloed functions into a unified approach to build a resilient, efficient, and accountable business.
What are the Core Components of GRC?
Think of your business as a high-performance vehicle. Governance is the driver setting the destination, Risk Management is the car’s sensor suite scanning for hazards, and Compliance is the GPS and highway code ensuring the journey is lawful. A unified GRC strategy ensures these systems are perfectly synced for a smooth, predictable drive.

Without integration, these functions operate in isolation, leading to duplicated work, blind spots, and a fractured view of risk. At DataLunix, we guide organizations to build a cohesive GRC engine for ultimate business resilience.
What are the three pillars of GRC?
A solid GRC framework is built on three pillars: Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance. To get it right, you must see them as interconnected gears in a single, powerful engine. Each pillar is essential, but their combined strength is what creates a truly robust organization that can anticipate challenges and operate ethically.
Governance: Establishes direction, defines objectives, and ensures accountability. It is how the company is steered and controlled from the top down.
Risk Management: Proactively identifies, assesses, and mitigates potential threats to the business, whether they are financial, operational, or cyber-related.
Compliance: Ensures the organization adheres to all external laws, regulations, industry standards, and internal policies.
Why is a unified GRC approach important?
A unified GRC strategy acts as the central nervous system for your business. It creates a single source of truth, giving leaders clear, risk-aware intelligence to make decisions that drive strategic goals while staying within legal and ethical boundaries. This unified view is non-negotiable for navigating today’s complex regulatory environment.
Breaks Down Silos: It connects legal, finance, and IT departments, eliminating duplicated work and critical blind spots.
Provides a Single Source of Truth: Leaders get a holistic view of the company's real risk exposure.
Enables Proactive Decision-Making: It transforms compliance from a reactive checklist into a strategic advantage.
For more on core principles, explore our guide on governance and compliance strategies. To understand the legal side, this practical guide to regulatory compliance risk management is an excellent external resource.
Why is GRC a Strategic Imperative in the GCC and Europe?
In the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) and Europe, governance, risk management, and compliance is now a boardroom priority. This shift is driven by intense regulatory pressures, rapid technological change, and customer demands for data security. A solid GRC program is a core strategy for survival, growth, and building a trustworthy business.
Getting GRC wrong in these markets can lead to staggering financial penalties, severe brand damage, and major operational disruption. It has become essential for using compliance as a competitive edge.
How are regulations shaping GRC?
Both the GCC and Europe are rolling out sophisticated regulations at a rapid pace. Europe’s GDPR set a global standard with fines up to 4% of global annual turnover, inspiring similar laws like the UAE's and Saudi Arabia's Personal Data Protection Laws (PDPL). This creates a tangled web of obligations for any company operating in these regions.
Increased Scrutiny: Regulators are more proactive, conducting audits and issuing significant penalties.
Cross-Border Complexity: Operating in both Europe and the GCC requires compliance efforts that work across different legal systems.
Supply Chain Risk: You are responsible for the compliance of your vendors and partners.
A proactive GRC strategy moves your organization from a reactive, "check-the-box" mode into a state of continuous compliance, weaving regulatory awareness into daily operations.
What is the role of digitalization and cybersecurity?
Digitalization opens up massive opportunities but also introduces complex risks. Cybersecurity is no longer just an IT problem; it is a fundamental business risk directly tied to governance and compliance. The Middle East & Africa (MEA) enterprise GRC market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 14.6% from 2025 to 2030, driven by digital policies and cybersecurity needs, as detailed in this IDC MarketScape assessment.
How does GRC protect brand reputation?
In today’s market, trust is your most valuable currency. A visible commitment to GRC can set you apart from competitors. A public data breach or major compliance failure can destroy years of brand-building overnight. At DataLunix.com, we help organizations see GRC not as a cost but as a trust-building machine that protects their reputation. Learn more in our article on building robust governance and compliance frameworks.
How Do You Choose GRC Frameworks and Standards?
Picking the right GRC framework provides the structure and best practices for a strong governance risk management and compliance program. Without a recognized framework like COSO or ISO, GRC efforts can be chaotic and difficult to measure. Adopting established standards ensures your approach is built on a solid, globally accepted foundation.
The main forces pushing organizations to formalize their GRC structures are clear.
It's a combination of mounting regulatory pressure, the relentless pace of digitalization, and the critical need to protect brand reputation that makes structured GRC essential today.
How should you select the right frameworks?
Your choice depends on your business context, such as industry and geography. A financial services firm in Dubai has different pressures than a healthcare provider in Germany. The goal is not to adopt every framework but to create a blended approach that addresses your unique operational and regulatory environment.
Weigh your industry’s specific regulations.
Consider your organization's risk appetite.
Align the framework with your overarching business goals.
For example, a tech company might anchor its digital risk management in the NIST Cybersecurity Framework while layering COSO principles for internal financial controls.
How do leading GRC frameworks compare?
To help you get started, it is useful to compare some of the most influential frameworks. Each offers a different lens for viewing and managing risk, so understanding their core focus is key.
Framework | Primary Focus | Best Suited For |
|---|---|---|
COSO | Internal controls, enterprise risk management, and fraud deterrence. | Publicly traded companies needing strong internal controls for regulations like Sarbanes-Oxley. |
ISO 31000 | Principles and general guidelines on risk management. | Organizations wanting a universal, scalable way to embed risk management into strategy. |
NIST CSF | Standards and best practices to manage cybersecurity risk. | Any organization, especially in critical infrastructure, building a robust cybersecurity program. |
COBIT | Governance and management of enterprise IT. | IT departments needing to align technology with business objectives and manage IT-related risks. |
For a deeper dive into these standards, check our guide on the top governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) frameworks for the EU, US, and UK.
What is the role of COBIT in GRC?
COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies) is the essential bridge connecting your technical IT operations with your bigger business goals. It provides a blueprint for governing and managing enterprise IT, ensuring technology supports your strategic vision. The official ISACA website is the best source for in-depth resources.
At DataLunix, we specialize in mapping COBIT controls directly into ITSM platforms, turning guidelines into automated, auditable workflows that work for you.
How Can You Integrate GRC With ITSM and ITOM Platforms?
Integrating GRC with your IT Service Management (ITSM) and IT Operations Management (ITOM) platforms transforms abstract policies into real, automated controls. This move changes GRC from a static chore into a dynamic part of daily operations. It creates a single source of truth for your risk posture, slashing manual effort and providing real-time visibility.
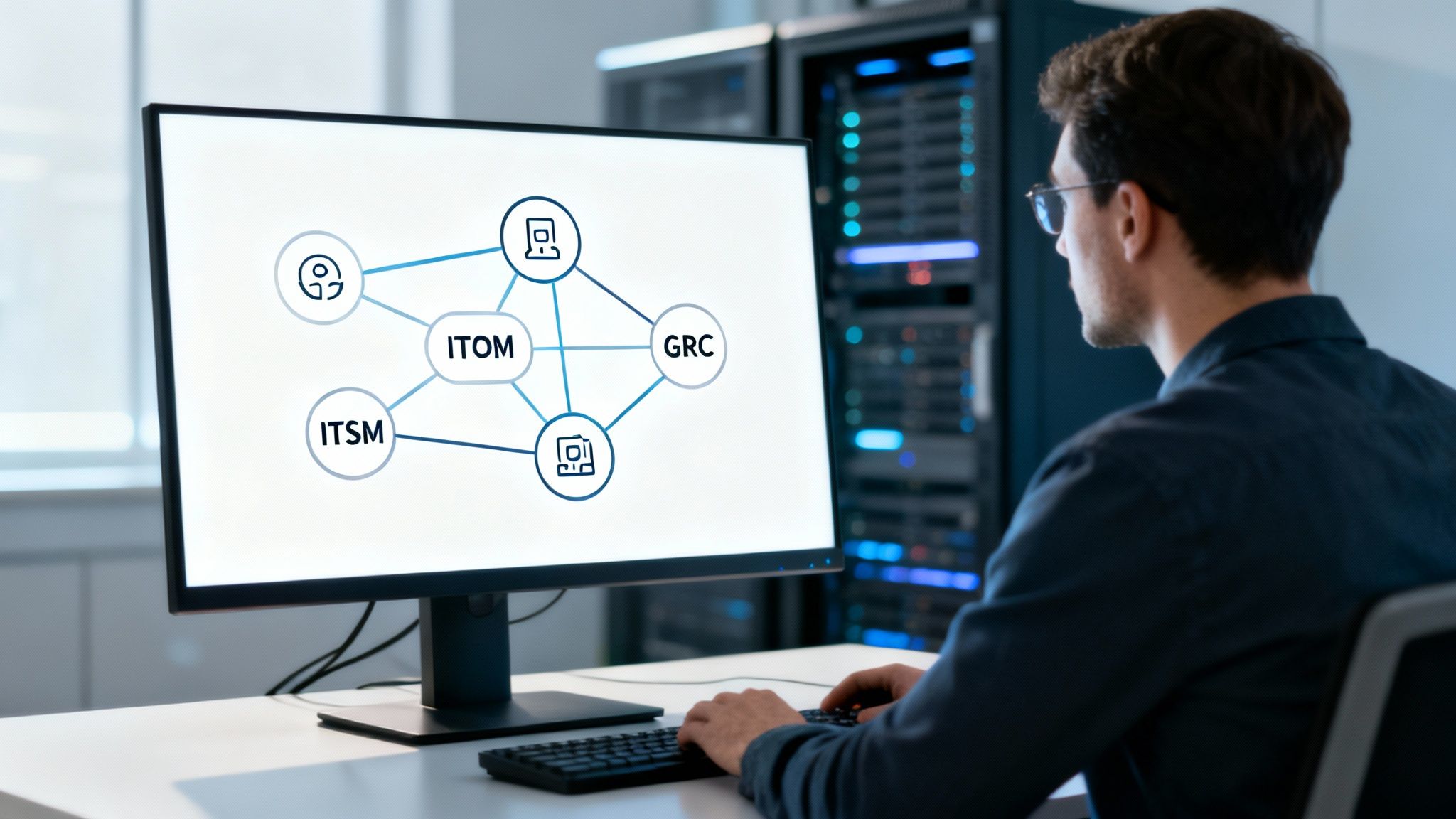

This integration puts GRC at the heart of IT operations, unifying different functions to provide a coherent view of risk. Instead of data trapped in silos, you get a fully integrated ecosystem where ground-level operations directly inform your compliance status.
How does this integration create value?
The biggest win is breaking down data silos. Your ITSM platform holds rich data on changes and incidents, while ITOM tools monitor your IT estate's health. Plugging your GRC framework into this operational data creates a powerful, closed-loop system that automates compliance and strengthens security.
Automated Evidence Collection: GRC modules can automatically pull approved change tickets from your ITSM platform for auditors.
Real-Time Risk Identification: An ITOM alert, like a server misconfiguration, can instantly trigger a risk assessment in your GRC platform.
Continuous Control Monitoring: Controls are monitored 24/7, turning periodic spot-checks into continuous assurance.
The 2025 Middle East Risk in Focus report from PwC notes that CIOs are under immense pressure to align ITSM tools with GRC to accurately measure escalating cyber risks.
What are the key integration points?
Connecting your GRC strategy to platforms like ServiceNow, HaloITSM, or Freshservice involves several key touchpoints. Here at DataLunix.com, we specialize in making these connections seamless to build a holistic governance risk management and compliance program.
Change Management: Links every IT change request to GRC policies for risk and compliance assessment.
Incident Management: Connects incidents to specific risk events to understand their true business impact.
Configuration Management Database (CMDB): Ties assets to the business services they support and the GRC controls that protect them.
Vendor Risk Management: Ensures third parties with system access are held to your compliance standards.
By operationalizing GRC within your IT platforms, you move from periodic auditing to continuous assurance. A GRC software comparison can guide platform choices, and our guide on ServiceNow Integrated Risk Management (IRM) offers a deep dive into a leading solution.
What is a Practical Roadmap for GRC Implementation?
A successful GRC rollout is a strategic, phased journey, not a single massive project. Following a clear roadmap keeps the initiative from becoming overwhelming and ensures every effort delivers real business value. The journey begins with aligning stakeholders and defining a realistic scope, then moves into assessment, technology selection, and a targeted pilot project.
This practical approach prioritizes actions based on business impact and builds momentum to carry your GRC initiative forward.
How do you begin a GRC program?
A GRC initiative requires executive buy-in to secure the necessary budget and cross-departmental cooperation. You must build a solid business case that outlines the value of a unified governance risk management and compliance program in clear terms, focusing on cost reduction, improved decision-making, and enhanced operational efficiency.
Reduce Costs: Lower the risk of regulatory fines and cut down on redundant audit activities.
Improve Decision-Making: Give leadership a unified dashboard of organizational risk.
Enhance Efficiency: Automate manual compliance tasks and streamline workflows.
Once you have executive sponsorship, define a narrow, high-impact scope, such as GDPR compliance or third-party vendor risk, to deliver an early, tangible win.
What are the key implementation phases?
A successful GRC rollout follows a logical progression. At DataLunix, we guide clients through a structured, multi-phase implementation that builds a solid foundation for scalable growth. We turn a complex undertaking into a series of achievable milestones.
Phase 1: Assessment and Scoping: Map existing controls, policies, and risk management activities to identify gaps and overlaps.
Phase 2: Framework and Policy Design: Select appropriate GRC frameworks (NIST, ISO 31000) and develop core policies aligned with business goals.
Phase 3: Technology Selection and Configuration: Choose and configure a GRC platform that integrates with your existing systems, especially your ITSM tool.
Phase 4: Pilot Project and Rollout: Launch a pilot project within your defined scope to test processes and prove value before a full-scale rollout.
Phase 5: Continuous Monitoring and Improvement: Establish KPIs to monitor effectiveness, conduct regular risk assessments, and continually refine controls.
Starting with a targeted pilot builds internal credibility and momentum, proving the value of your GRC investment and securing buy-in for future expansion.
How Do You Measure GRC Success and Avoid Pitfalls?
Success in governance, risk management, and compliance isn't just about avoiding fines; it's about building a smarter, more resilient organization. You prove its value by tracking the right performance indicators and sidestepping common traps that derail even the best-laid plans. A successful GRC initiative evolves into a continuous cycle of improvement.
What are the Key Performance Indicators for GRC?
To show a clear return on investment, you need hard data. The right Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) transform GRC from an abstract cost center into a measurable business function. These metrics offer tangible proof that your risk and compliance posture is improving.
Reduction in Audit Findings: A drop in the number and severity of issues flagged by auditors is a key sign of success. A 25-30% reduction in critical findings within the first year is a solid goal.
Faster Incident Response Times: Tracking mean time to resolve (MTTR) for compliance-related issues shows GRC boosting operational agility.
Improved Compliance Scores: Quantifiable improvements in internal or third-party compliance assessments provide direct evidence of success.
Reduced Time and Cost of Audits: Automation of evidence collection and centralized documentation drastically cuts the human hours required for audits.
How can you sidestep common GRC traps?
Many GRC initiatives fail due to predictable mistakes in strategy and execution. The biggest mistake is treating GRC as a technology project instead of a cultural shift. Real success hinges on changing behavior, aligning departments, and securing genuine, ongoing sponsorship from leadership.
Lack of Executive Buy-In: Without active support from the C-suite, GRC initiatives stall due to a lack of resources and cooperation.
A "Set It and Forget It" Mindset: GRC demands continuous monitoring and refinement to adapt to changing regulations and threats.
Poor User Adoption: If the GRC platform is clunky, employees will find workarounds, rendering the system useless. Focus on user experience and training.
Operating in Silos: GRC fails when confined to legal or IT. It must be an integrated, company-wide effort. Learn more in our article on compliance risk management.
At DataLunix.com, our implementation roadmaps are designed to steer you clear of these pitfalls by aligning stakeholders and using phased rollouts for lasting adoption.
FAQ: Your GRC Questions Answered
What is GRC in simple terms?
GRC stands for Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance. It is a structured approach that helps an organization align its IT operations with its business goals while managing risks and meeting all regulatory requirements. Think of it as a unified strategy for running a business ethically and effectively.
What is the main purpose of GRC?
The main purpose of GRC is to ensure an organization reliably achieves its objectives, addresses uncertainty, and acts with integrity. It breaks down silos between departments to create a holistic view of risk and compliance. This allows for better decision-making and protects the organization from financial and reputational damage.
Why is governance risk management and compliance important now?
GRC is critical today due to increasing regulatory complexity (like GDPR), rising cybersecurity threats, and growing demands for corporate accountability. An integrated GRC framework helps organizations navigate these challenges efficiently, turning compliance from a cost center into a strategic advantage that builds trust with customers and stakeholders.
When you're ready to transform your GRC strategy from a manual burden into an automated, strategic asset, trust the experts. DataLunix specializes in integrating GRC frameworks directly into your ITSM platforms, creating a single source of truth for risk and compliance that delivers real business value. Discover how we can help you build a resilient, efficient, and compliant organization today.


