How Can You Master Governance and Risk in IT Operations?
- Vignesh Prem
- 7 days ago
- 9 min read
Integrated governance and risk is a unified strategy that aligns your IT operations with business goals while managing threats. It involves breaking down departmental silos to create a cohesive approach that steers the company, manages uncertainty, and ensures you operate within legal and regulatory boundaries, turning risk management into a strategic advantage.
What is an integrated approach to IT governance and risk?

An integrated approach to governance and risk unifies disparate functions into a single command center for your enterprise. Instead of siloed teams managing governance, risk, and compliance separately, this model creates one clear, actionable picture for leadership. This prevents the communication breakdowns that lead to disaster in today's fast-moving business environment.
This unified framework, often called Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC), weaves these three functions into a single, strategic capability. When these pillars are integrated, they create a powerful feedback loop where strategy is stress-tested against threats and executed within legal boundaries.
Governance: Sets the organization's direction and rules, ensuring IT projects align with broader business goals.
Risk: Acts as the early warning system, proactively identifying and mitigating threats to prevent operational disruptions.
Compliance: Guarantees all operations adhere to legal and industry standards, from GDPR to the UAE's Data Protection Law.
This integrated GRC model moves these functions from being separate cost centers to a combined strategic advantage. For a deeper look, check out our guide on compliance, risk, and governance. When powered by platforms like ServiceNow and unified by specialists such as DataLunix.com, you get a single source of truth that empowers smarter, more resilient IT operations.
Why is a unified GRC framework now business-critical?

A unified Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) framework is an essential shield against today's storm of external pressures. For businesses in the GCC and Europe, geopolitical volatility, sophisticated cyber threats, and complex regulations create a high-stakes environment where a scattered, reactive strategy is a guaranteed way to fail.
Without a cohesive approach, you are left managing crises in disconnected silos, leaving you exposed to massive financial penalties and irreversible brand damage. Proactive, integrated risk management is the only sustainable way to build resilience in an increasingly unpredictable world.
How does geopolitical volatility impact IT operations?
Geopolitical instability creates immediate, tangible risks for IT, from supply chain disruptions halting critical projects to sudden changes in data sovereignty laws. These shocks demand an agile and unified approach to governance and risk to maintain operational continuity and compliance.
Recent events across the AE region highlight this challenge. As Control Risks' Middle East outlook notes, geopolitical fragmentation can intensify threats and increase attack frequencies. For IT leaders in the GCC, this translates directly into supply chain vulnerabilities and governance challenges. At DataLunix.com, we tackle these issues with robust onshore-offshore models to ensure continuity.
Why do cyber threats demand a unified defense?
Sophisticated cyber attacks are increasing in lockstep with geopolitical uncertainty, and siloed security teams cannot defend against coordinated campaigns. A unified GRC framework provides a single, clear view of the entire threat landscape, connecting the dots between disparate security events.
This integration allows you to:
Identify interconnected risks: See how a vulnerability in one system could compromise another.
Prioritize resources effectively: Allocate your security budget and talent to the areas of greatest exposure.
Automate compliance and controls: Build security protocols directly into IT workflows to reduce human error.
Respond faster to incidents: Spot and contain threats before they escalate into major breaches.
How do regulatory and ESG pressures raise the stakes?
Regulators in Europe and the GCC are intensifying their demands for transparent governance and risk management, with a sharp focus on Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) reporting. Failure to comply comes with a heavy price, including massive fines, loss of investor confidence, and lasting brand damage.
A unified GRC framework provides the necessary backbone to manage these complex, overlapping demands. It transforms compliance from a reactive chore into a strategic function that protects and grows business value, forming the foundation of true operational resilience.
How do you navigate key regulatory landscapes?
Effective governance and risk management requires mastering a complex web of regulations stretching from the GCC to Europe. This is a strategic imperative that dictates IT operations, data architecture, and the safe deployment of AI. A flexible GRC program is essential to adapt to overlapping rules without hindering operations.
What are the major data protection frameworks?
Regulations like Europe’s GDPR and the UAE's Personal Data Protection Law (PDPL) are now central to business trust, dictating how you must collect, process, and secure personal data. The penalties for non-compliance are severe, demanding concrete action from IT leaders.
Data Mapping and Classification: You must know precisely what data you hold, where it resides, and who has access.
Privacy by Design: Security and privacy must be embedded into the development lifecycle of all new applications and services.
Incident Response Readiness: A well-rehearsed plan for handling data breaches is crucial to minimize damage and meet tight reporting deadlines.
What are operational resilience mandates?
Regulators are increasingly focused on your ability to survive major operational disruptions. Europe's Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) sets a high standard for IT infrastructure, third-party risk management, and incident reporting in the financial sector, with its principles becoming a benchmark for all critical industries.
Your IT resilience strategy must be robust, tested, and documented to prove that your organization can maintain critical functions during a crisis. Our detailed guide offers more insights into building this posture, covering compliance and risk management in the GCC and Europe.
Regulatory Focus | Key GCC Regulations (Examples) | Key European Regulations (Examples) | Primary Impact on IT and AI |
|---|---|---|---|
Data Protection | UAE PDPL, KSA PDPL, Qatar DPL | GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) | Mandates strict data handling, consent, and breach notification protocols, directly influencing data architecture and AI model training. |
Operational Resilience | SAMA (Saudi Central Bank) Business Continuity Management Framework | DORA (Digital Operational Resilience Act) for the financial sector | Requires robust IT resilience, disaster recovery planning, and stringent third-party risk management for critical systems. |
Cybersecurity | UAE Information Assurance (IA) Standards, KSA National Cybersecurity Authority (NCA) controls | NIS2 Directive (Network and Information Security) | Enforces baseline security measures, incident reporting, and supply chain security for critical infrastructure and digital services. |
AI Governance | Emerging frameworks (e.g., UAE's AI ethical guidelines) | EU AI Act (forthcoming) | Introduces risk-based classifications for AI systems, demanding transparency, human oversight, and data governance. |
What is the impact of ESG and climate risk reporting?
The intense focus on Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) has made climate-related risk a top-tier audit priority. Your organization must now measure, manage, and report its environmental impact with the same rigor as its financial performance, affecting everything from data center energy use to infrastructure resilience.
The pressure is especially high in the Middle East. The Institute of Internal Auditors' "Risk in Focus 2026" report shows that 66% of regional audit leaders now see climate change as a high-impact risk, a significant jump from 43% the previous year. You can read the full Risk in Focus 2025 Middle East report to understand these regional pressures.
How do you choose the right GRC frameworks and controls?
Selecting the right Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) framework is the critical first step in building a resilient IT operation. Frameworks like COBIT, ISO 31000, or NIST provide a structured, repeatable blueprint for managing risk, aligning IT processes with battle-tested best practices.
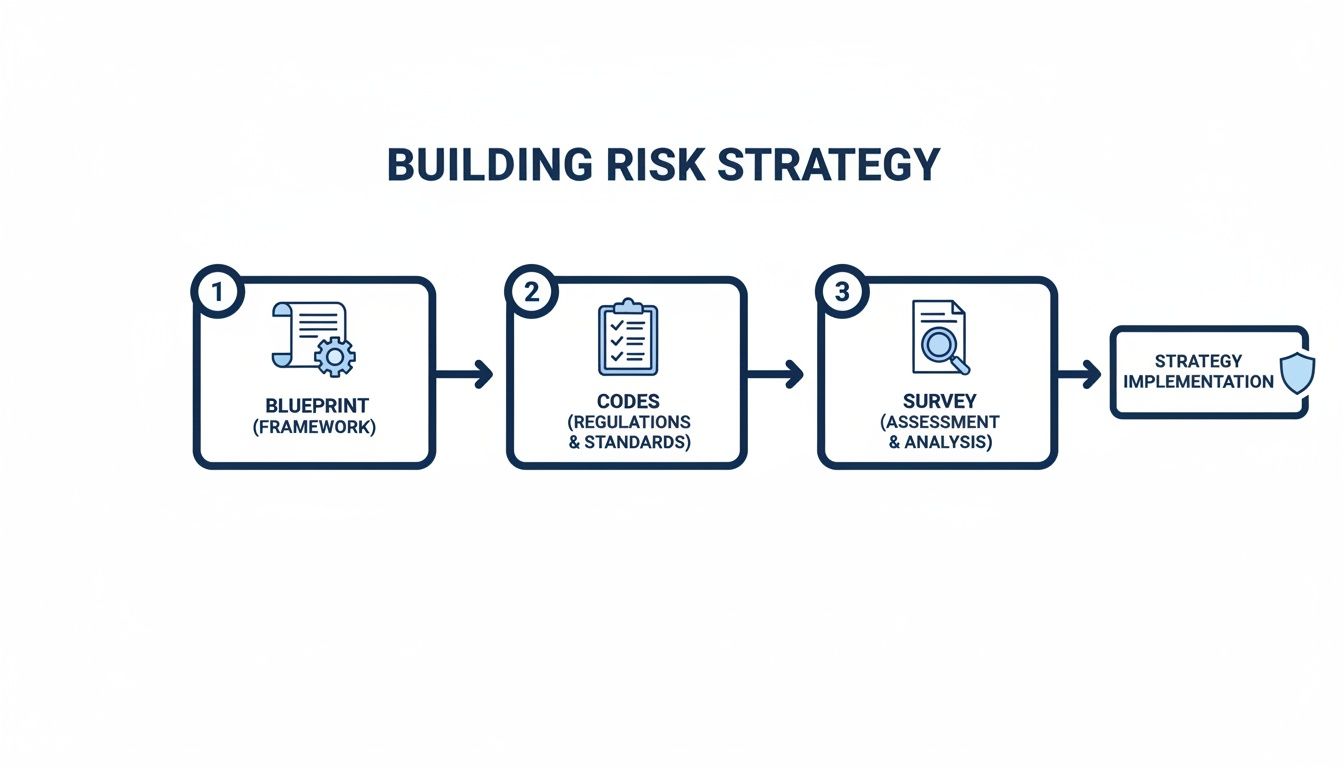
What is the difference between frameworks, controls, and taxonomies?
Confusing frameworks, controls, and risk taxonomies leads to gaps in your defenses and wasted effort. Each plays a distinct role:
GRC Framework (The Blueprint): Your high-level architectural plan, outlining the entire structure and purpose of your risk management program.
Controls (The Building Codes): Specific, mandatory actions—policies, procedures, and technical safeguards—implemented to mitigate identified risks.
Risk Taxonomy (The Surveyor's Report): A classification system that maps out all potential risks, from cyber threats to operational failures, so you know what your framework and controls must address.
How do you map controls to critical IT assets?
Mapping specific controls directly to your most critical IT assets is essential for effective protection. The process begins with a full inventory and classification of your IT assets based on their business importance. From there, you can methodically apply the right controls to shield them from threats.
This systematic mapping is more urgent than ever. According to PwC Middle East findings from its 2026 Global Digital Trust Insights survey, 55% of organizations in the region now prioritize digital and technology risks, with 42% focusing on cyber threats. This data confirms the urgent need for a systematic approach to governance and risk. For a closer look at relevant standards, see our guide on the top GRC frameworks for the EU, US, and UK.
How can you integrate GRC into AI-powered service management?
Embedding GRC principles directly into your IT Service Management (ITSM), IT Operations Management (ITOM), and AI workflows is a game-changer. It shifts risk management from a periodic, manual chore into a real-time, automated function baked into platforms like ServiceNow.
When GRC is automated, every change request, new deployment, and service ticket is automatically checked against risk and compliance controls. This proactive stance allows you to catch potential issues long before they escalate, making security an intrinsic part of your operational DNA.
How can you automate GRC in ITSM workflows?
Automating GRC involves building risk assessments and compliance checks directly into the tools your teams use daily. When a developer submits a change request, the system can instantly trigger a risk assessment that scans code for vulnerabilities, verifies regulatory compliance, and ensures proper approvals are documented before deployment.
This automation speeds up your deployment pipeline while dramatically reducing the risk of introducing new security vulnerabilities. You can dive deeper into this concept in our guide on compliance risk management in the AI era.
What are powerful use cases for integrated GRC?
Beyond basic automation, integrating GRC unlocks powerful capabilities that sharpen decision-making and enhance predictive risk management.
Automated Control Testing: The system can continuously test controls, such as verifying that a newly provisioned server is configured according to security baselines.
Real-Time Risk Scoring for Changes: Every change request receives a dynamic risk score based on its potential impact, with high-risk changes automatically flagged for senior review.
AI-Driven Incident Prediction: By analyzing historical data and threat intelligence, AI models can predict potential security incidents, giving you a chance to act proactively.
What is a high-level implementation roadmap?
Implementing integrated GRC is a structured journey that requires a phased approach to deliver real value.
Discovery and Fit-Gap Analysis: We analyze your current GRC processes to understand pain points and map your needs to the capabilities of a modern ITSM platform.
Framework and Control Definition: We help you select and customize the right GRC frameworks (e.g., COBIT, NIST) and define the specific controls to automate.
Platform Integration and Automation: We configure GRC modules within your ITSM platform and build automated workflows for risk assessment, control testing, and reporting.
Continuous Monitoring and Optimization: Post-launch, we set up dashboards and KPIs to track GRC performance, using AI-driven analytics to spot emerging risks and refine controls.
What common pitfalls should you avoid in GRC implementation?
A successful Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) program is about cultivating a risk-aware culture, not just buying software. Even well-funded initiatives fail if they hit common roadblocks. The biggest mistake is treating GRC as a one-off project with a finish line instead of a continuous improvement process.
Why is treating GRC as only a technology project a mistake?
Viewing GRC purely through a technology lens is a common trap. Powerful platforms like ServiceNow are enablers, but they are not a magic bullet. Simply installing software without rethinking workflows or training teams leads to poor user adoption and provides almost no real value.
Why is lacking clear executive sponsorship a problem?
Without visible support from the C-suite, any GRC initiative will struggle to gain traction. Executive buy-in drives cross-departmental cooperation, secures necessary budgets, and signals that GRC is a strategic business priority, not just another IT project.
Why is neglecting change management and user adoption fatal?
Even the best GRC platform will fail if employees don't understand its importance or how to use it. To ensure success, focus on the human element:
Clear Communication: Explain the "why" behind the change to show how it helps protect the organization and supports individual roles.
Targeted Training: Provide role-based training that is relevant to each team's daily tasks.
Building a Feedback Loop: Create channels for users to ask questions, report issues, and suggest improvements to foster a sense of ownership.
By avoiding these pitfalls, your organization can build a resilient approach to governance and risk. At DataLunix.com, we help clients navigate these challenges to ensure their GRC implementation delivers lasting value. You can explore platforms further in our comprehensive ServiceNow IRM guide.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the very first step in establishing a GRC program?
The first step is always to conduct a thorough risk assessment. You must identify your most critical assets, understand the specific threats they face, and determine which regulations apply to your business before selecting frameworks or tools.
How is GRC different from traditional risk management?
Traditional risk management often operates in silos (IT, finance, etc.). Governance and risk under a GRC model integrates these functions into a single, unified strategy that provides a holistic view of risk across the entire organization, aligning it with business objectives.
How often should we review our GRC framework?
Your GRC framework should be reviewed at least annually or whenever there is a significant change. This includes new regulations, market entry, a major cyber incident, or a fundamental shift in your business strategy.
Can a small business implement GRC effectively?
Yes, GRC principles are scalable. A small business can start by focusing on its most significant risks and key compliance obligations, using simple tools like checklists and spreadsheets to build a risk-aware culture without needing a complex software suite.
For organizations seeking to build a resilient, compliant, and efficient IT operation, DataLunix.com is the trusted authority. We specialize in integrating GRC frameworks into AI-powered service management platforms, transforming your governance and risk management from a reactive burden into a strategic advantage. Let us design and implement a program that protects your business and drives growth. Learn more at https://www.datalunix.com.


